- Overview
- Documents
validate.js is a lightweight JavaScript form validation library inspired by CodeIgniter. No dependencies, just over 2kb gzipped, and customizable!
Features
- Validate form fields from over a dozen rules
- No dependencies
- Customizable messages
- Supply your own validation callbacks for custom rules
- Chainable customization methods for ease of declaration
- Conditionally validate certain form fields
- Works in all major browsers (even IE6!)
- Modeled off the CodeIgniter form validation API
Source: rickharrison.github.io
1. INCLUDE JS FILES
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.6.4/jquery.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="validate.min.js"></script>
2. HTML
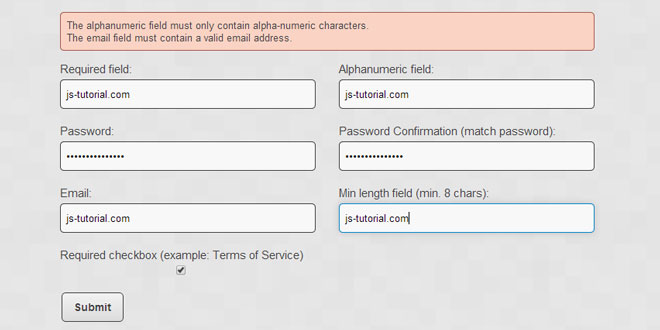
<form name="example_form" action="#" method="POST"> <label for="req">Required field:</label> <label for="alphanumeric">Alphanumeric field:</label> <input name="req" id="req"> <input name="alphanumeric" id="alphanumeric"> <label for="password">Password:</label> <label for="password_confirm">Password Confirmation (match password):</label> <input name="password" id="password" type="password"> <input name="password_confirm" id="password_confirm" type="password"> <label for="email">Email:</label> <label for="minlength">Min length field (min. 8 chars):</label> <input name="email" id="email"> <input name="minlength" id="minlength"> <label for="tos_checkbox">Required checkbox (example: Terms of Service)</label> <input name="tos_checkbox" id="tos_checkbox" type="checkbox"> <button class="button gray" type="submit" name="submit">Submit</button> </form>
3. JAVASCRIPT
new FormValidator('example_form', [{
name: 'req',
display: 'required',
rules: 'required'
}, {
name: 'alphanumeric',
rules: 'alpha_numeric'
}, {
name: 'password',
rules: 'required'
}, {
name: 'password_confirm',
display: 'password confirmation',
rules: 'required|matches[password]'
}, {
name: 'email',
rules: 'valid_email'
}, {
name: 'minlength',
display: 'min length',
rules: 'min_length[8]'
}, {
name: 'tos_checkbox',
display: 'terms of service',
rules: 'required'
}], function(errors, evt) {
if (errors.length > 0) {
// Show the errors
}
});
new FormValidator(formName, fields, callback)
The FormValidator object is attached to the window upon loading validate.js. After creation, it will validate thefields on submission of the form named formName.
The formName passed in to validate must be the exact value of the name attribute of the form
<form name="example_form"></form>
An array of fields will be used to perform validation on submission of the form. The array must contain objects containing these properties:
-
name (required) - The name attribute of the element.
<input name="email" />
-
display (optional) - The name of the field as it appears in error messages. If not present in the object, thename parameter will be used.
Example: If your field name is user, you may choose to use a display of "Username."
-
rules (required) - One or more rules, which are piped together.
Example - required|min_length[8]|matches[password_confirm]
-
depends (optional) - A function that runs before the field is validated. If the function returns false, the field is never validated against the declared rules.
depends: function(field) { return Math.random() > .5; }
A callback will always be executed after validation. Your callback should be ready to accept two parameters.
-
errors - An array of errors from the validation object. If the length > 0, the form failed validation
This array will contain javascript objects with up to three properties:
- id: The id attribute of the form element
- name: The name attribute of the form element
- message: The error message to display
- rule: The rule that prompted this error - event - If the browser supports it, the onsubmit event is passed in.
function(errors, event) {
if (errors.length > 0) {
var errorString = '';
for (var i = 0, errorLength = errors.length; i < errorLength; i++) {
errorString += errors[i].message + '<br />';
}
el.innerHTML = errorString;
}
}
4. AVAILABLE RULES
| Rule | Description | Parameter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| required | returns false if the form element is empty. | no | |
| matches | returns false if the form element value does not match the one in the parameter. | yes | matches[other_element] |
| valid_email | returns false if the form element value is not a valid email address. | no | |
| valid_emails | returns false if any value provided in a comma separated list is not a valid email. | no | |
| min_length | returns false if the form element value is shorter than the parameter. | yes | min_length[6] |
| max_length | returns false if the form element value is longer than the parameter. | yes | max_length[8] |
| exact_length | returns false if the form element value length is not exactly the parameter. | yes | exact_length[4] |
| greater_than | returns false if the form element value is less than the parameter after using parseFloat. | yes | greater_than[10] |
| less_than | returns false if the form element value is greater than the parameter after using parseFloat. | yes | less_than[2] |
| alpha | returns false if the form element contains anything other than alphabetical characters. | no | |
| alpha_numeric | returns false if the form element contains anything other than alpha-numeric characters. | no | |
| alpha_dash | returns false if the form element contains anything other than alphanumeric characters, underscores, or dashes. | no | |
| numeric | returns false if the form element contains anything other than numeric characters. | no | |
| integer | returns false if the form element contains anything other than an integer. | no | |
| decimal | returns false if the form element contains anything other than a decimal. | no | |
| is_natural | returns false if the form element contains anything other than a natural number: 0, 1, 2, 3, etc. | no | |
| is_natural_no_zero | returns false if the form element contains anything other than a natural number, but not zero: 1, 2, 3, etc. | no | |
| valid_ip | returns false if the supplied IP is not valid. | no | |
| valid_base64 | returns false if the supplied string contains anything other than valid Base64 characters. | no | |
| valid_credit_card | returns false if the supplied string is not a valid credit card | no | |
| valid_url | returns false if the supplied string is not a valid url | no | |
| is_file_type | returns false if the supplied file is not part of the comma separated list in the paramter | yes |
is_file_type[gif,png,jpg] |
5. AVAILABLE METHODS
setMessage
validator.setMessage(rule, message)
All of the default error messages are located at the top of validate.js in a defaults object. If you wish to change a message application wide, you should do so in the source code. If you would like to change a message for a form, use this method on your instance of the FormValidator object. When setting a new message, you should pass in %s, which will be replaced with the display parameter from the fields array
validator.setMessage('required', 'You must fill out the %s field.');
registerCallback
validator.registerCallback(rule, callback)
Used to pair a custom rule in the fields array with a callback to be executed upon validation.
validator.registerCallback('check_email', function(value) {
if (emailIsUnique(value)) {
return true;
}
return false;
});
registerConditional
validator.registerConditional(name, callback)
An alternate syntax for declaring depends functions, which determine whether or not to validate a given field.
{
name: 'first_name',
rules: 'required',
depends: 'checkForRandomNumber'
}
validator.registerConditional('checkForRandomNumber', function(field) {
return Math.random() > .5;
});
6. CUSTOM VALIDATION RULES
validate.js supports the ability for you to include your own validation rules. This will allow you to extend validate.js to suit your needs. A common example of this would be checking the strength of a password.
First, you need to add another rule to the field. It must always be prefaced with "callback_"
rules: 'required|callback_check_password'
Then you must call registerCallback on your instance of the FormValidator with the name of your custom rule and a function taking one parameter. This function will be called with one argument, the value of the field. If the value passes your custom validation, return true, otherwise return false. You can set a message for this rule using the setMessage method as described below.
validator.registerCallback('check_password', function(value) {
if (passwordIsStrong(value)) {
return true;
}
return false;
})
.setMessage('check_password', 'Please choose a stronger password using at least 1 number.');
Callbacks behave according to the following rules:
#1. If the required rule is present, a callback will be fired once all other validation rules pass.
#2. If the field is not required and it is empty, the callback will not be called unless condition #3 is met.
#3. A callback will always be called if it is preceded by an '!' i.e. rules: '!callback_myCustomCallback'
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial