- Overview
- Documents
interact.js is a powerful, flexible, snappable drag and drop, resizing and multi-touch gestures for modern browsers (and also IE8+)
- snapping to a grid, custom anchors or paths.
- cross browser and device, supporting {Chrome,Firefox,Opera}' '{mobile,desktop}', ' and Internet Explorer 8+
- interaction with SVG elements
- introducing 0 additional DOM elements
- having(a). fluent ().interface
Example
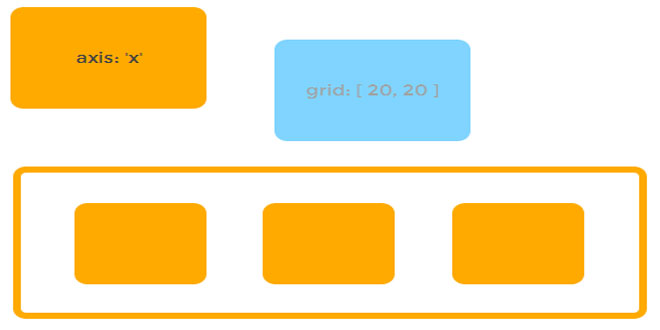
// snap to the corners of the specified grid
interact.snap({
mdoe: 'grid',
grid: {
x: 100,
y: 5
},
gridOffset: {
x: 20,
y: 10
},
range: Infinity // can also use -1 which gets changed to Infinity
});
var // x and y to keep the position that's been dragged to
x = 0,
y = 0,
// vendor prefixes (prefices?)
transformProp = 'transform' in document.body.style?
'transform': 'webkitTransform' in document.body.style?
'webkitTransform': 'mozTransform' in document.body.style?
'mozTransform': 'oTransform' in document.body.style?
'oTransform': 'msTransform';
// make an Interactable of the document body element
interact(document.body)
// make a draggable of the Interactable
.draggable({
// on(drag)move
// could also have done interact(document.body).draggable(true).ondragmove = function...
onmove: function (event) {
x += event.dx;
y += event.dy;
// translate the document body by the change in pointer position
document.body.style[transformProp] = 'translate(' + x + 'px, ' + y + 'px)';
}
})
// but you should really add listeners like this which lets you add multiple listeners
.on('dragend', function (event) {
console.log('dragged a distance of ' +
Math.sqrt(event.dx*event.dx + event.dy*event.dy) +
' pixels to ' + event.pageX + ', ' + event.pageY);
});
// or you could listen to InteractEvents for every Interactable
interact.on('dragstart', function (event) {
console.log('starting drag from ' + event.x0 + ', ' + event.y0);
});
Usage
Pass the element you want to interact with or a CSS selector string to interact. That returns an object with methods, notably draggable, resizable, gesturable, dropzone which let you allow or disallow the related actions and on which let's you add event listeners for InteractEvents and any DOM event. The InteractEvent types are {drag,resize,gesture}{start,move,end}', ' dragenter, dragleave anddrop when dragging over dropzones.
Details
Interactables
The interact function adds mouse or touch event listeners to the object and returns an Interactableobject which has several methods and properties to configure how it behaves and what it can do. These methods have a fluent interface so method calls can be chained nicely.
For example, to make a DOM element dragagble and resizable you can call the Interactable#set with an object with the properties you want to set
interact(document.getElementById('anElement'))
.set({
draggable: true,
resizable: true
});
or you can call each {action}able method with the options for each.
interact(document.getElementById('anElement'))
.draggable (true)
.resizable(true);
Acting
Now that the element has been made interactable, when it is clicked on or touched and then dragged, an action is determined depending on the input type and position of the event over the element. InteractEvents are then fired as the mouse/touch moves around the page until it is finally released or the window loses focus.
When a sequence of user actions results in an InteractEvent, that event type is fired and all listeners of that type which were bound to that Interactable or bound globally are called.
Even though InteractEvents are being fired, the element is not actually modified by interact.js at all. To do that, you need to add listeners for InteractEvents either to each Interactable or globally for all Interacables and style the element according to event data.
Listening
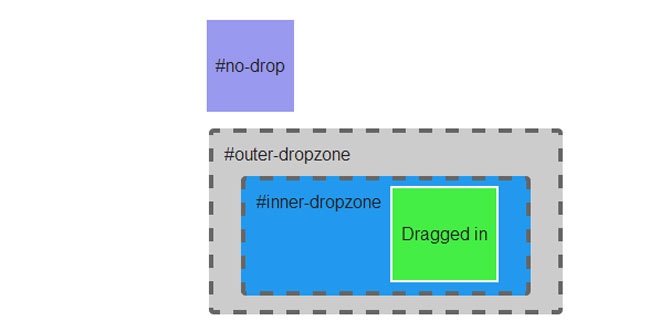
The InteractEvent types are {drag,resize,gesture}{start,move,end}, dragenter, dragleaveand drop when dragging over dropzones.
To respond to an InteractEvent, you must add a listener for its event type either directly to an interactable Interactable#on(eventType, listenerFunction) or globally for all events of that type interact.on('resizemove', resizeElement). The InteractEvent object that was created is passed to these functions as the first parameter.
InteractEvent properties include the usual properties of mouse/touch events such as pageX/Y, clientX/Y, modifier keys etc. but also some properties providing information about the change in cordinates and event specific data. The table below displays all of these events.
InteractEvent properties
| Common | |
|---|---|
| x0, y0 | Page x and y coordinates of the starting event |
| clientX0, clientY0 | Client x and y coordinates of the starting event |
| dx, dy | Change in coordinates of the mouse/touch * |
| target | The element that is being interacted with |
| Drag | |
|---|---|
| dragmove | |
| dragEnter | The dropzone this Interactable was dragged over |
| dragLeave | The dropzone this Interactable was dragged out of |
| dragenter, dragLeave | |
| draggable | The draggable that's over this dropzone |
| Drop | |
|---|---|
| draggable | The dragagble that was dropped into this dropzone |
| Resize | |
|---|---|
| axes | The axes the resizing is constrained to (x/y/xy) |
| Gesture | |
|---|---|
| touches | The array of touches that triggered the event |
| distance | The distance between the event's first two touches |
| angle | The angle of the line made by the two touches |
| da | The change in angle since previous event |
| scale | The ratio of the distance of the start event to the distance of the current event |
| ds | The change in scale since the previous event |
| box | A box enclosing all touch points |
* In interact move events, these are the changes since the previous InteractEvent. However, in end events, these are the changes from the position of the start event to the end event. In gesture events, coordinates are the averages of touch coordinates.
Interacting
To move an element in response to a dragmove, a listener can be bound that transforms the element accoding to dy and dx of the InteractEvent. It can also be done by having the element positioned absolute, fixedor relative and adding the change in coordinates to the top and left position of the element.
// Set element and listen for dragmove events
interact(element)
.draggable({
onmove: function(event) {
var elementStyle = event.target.style;
// Add the change in mouse/touch coordinates to the element's current position
elementStyle.left =
parseInt(elementStyle.left) + event.dx + "px";
elementStyle.top =
parseInt(elementStyle.top) + event.dy + "px";
});
More infomation at: http://interactjs.io/docs/
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial