User Rating: 0/5 ( 0 votes)
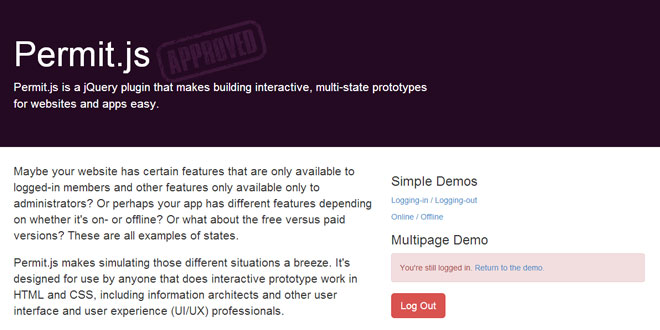
Maybe your website has certain features that are only available to logged-in members and other features only available only to administrators? Or perhaps your app has different features depending on whether it's on- or offline? Or what about the free versus paid versions? These are all examples of states.
Permit.js makes simulating those different situations a breeze. It's designed for use by anyone that does interactive prototype work in HTML and CSS, including information architects and other user interface and user experience (UI/UX) professionals.
Use Cases:
-
Authentication: Logged-Out / Logged-In
-
Membership: Free / Paid
-
Connectivity: Online / Offline
-
Roles: Writer / Editor / Publisher
-
Permissions: User / Moderator / Administrator
-
Content: English / French / Spanish
Take Your Prototypes to the Next Level
Use Permit.js to improve how your prototypes simulate complex, interactive behaviors.
Laughably Easy to Implement
No server side langauges necessary. Just load Permit.js, specify your states and apply some simple CSS.
Persistent
Permit.js persists across pages and sections of your website/app. "Issue a permit" and then surf around your entire site to get the full user experience for any of your states.
1. INCLUDE JS FILES
<script src="js/jquery-1.10.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="js/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script src="js/permit.min.js"></script>
2. JAVASCRIPT
$(document).ready(function(){
$.permit({
permits: ['free','premium','admin']
});
});
3. Create a "Permits Agent"
The optional "agent" will help you issue your permits and change between your states. Create a container with an ID of 'permit-agent'. When the script is instantiated, this container will be populated with a dropdown of your available permits. The agent issues a new permit when you click on an element with a class of 'permit-reissue'. You don't have to use the agent. If you prefer you can just issue or revoke permits using the plugin's helper classes.
<div>
<div id="permit-agent">
<!-- A dropdown with your states. -->
</div>
<button class="permit-reissue">Issue Permit</button>
</div>
4. Apply CSS
Permit.js creates several personalized helper classes based on your instantiation settings. All you need to do is apply a generic 'permit' class plus one of these personalized classes to your HTML markup. The following example shows how you might apply your CSS classes in the case of three states: free, premium, admin.
Custom Classes
<div class="permit permit-free">
<p>Visible to free users (only).</p>
</div>
<div class="permit permit-premium">
<p>Visible to premium users (only).</p>
</div>
<div class="permit permit-admin">
<p>Visible to admin users (only).</p>
</div>
Combining Classes
You can combine any of your custom classes. For example, if you want a block to show for free and premium users, but not admins, you could do the following:
<div class="permit permit-free permit-premium">
<p>Visible to free and premium users, but not admins.</p>
</div>
Default Classes
In addition, you can use .permit-all and .permit-none classes.
<div class="permit permit-none">
<p>Visible only when no permits have been issued (e.g, in a fully logged-out state).</p>
</div>
<div class="permit permit-all">
<p>Visible to all permit levels. Invisible if no permits are present.</p>
</div>
5. Additional Helper Classes and Advanced Usage
Permit.js provides additional helper classes that allow you to create even more complex, interactive experiences. Also see the plugin's API for even greater flexibility.
.permit-issue-[permitName]
Apply this class to an element (e.g. a button) to issue a permit. Replace [permitName] with one of the states you specified in the permits setting (e.g., permit-issue-premium). By default, the permit will be issued by clicking on the element. The permit that was in place prior to clicking on the element is revoked. You would use this in a variety of situations such as to simulate logging-in, upgrading, or for switching from online to offline mode. When using this class, two optional data attributes are also available: data-permit-trigger and data-permit-destination.
data-permit-trigger (optional)
You can change the default trigger from a click to any other jQuery mouse event by specifying it here. For example, you could change the event to 'hover' or 'dblclick'.
Example
<a class="permit-issue-premium" data-permit-trigger="hover">Upgrade</a>
data-permit-destination (optional)
Set this attribute to a url to redirect the user to that location after execution. You can set this to a local, relative path (e.g., homepage.html) or to a fully valid url (e.g., http://cnn.com). If you exclude this attribute, the current page will reload.
Example
<a class="permit-issue-premium" data-permit-destination="credit-card.html">Upgrade</a>
.permit-revoke-all
Apply this class to an element (e.g. a button) to revoke all permits. By default, it is trigger on a click event. You might use this to simulate a user log-out button. When using this class, you may use the same data-permit-trigger and data-permit-destination attributes described under .permit-issue-[permitName].
.permit-force
Apply this class, along with a custom data-messsage attribute, to replace the element's content with a custom message. For example, apply this class to replace a block of premium features with "Upgrade Now". The content in the data attribute gets injected using jQuery's html() method, so you may include html inside the message attribute.
data-permit-message
Set this attribute to specify the custom message that will appear if the required permit level(s) are not present.
<div class="permit permit-force permit-premium" data-permit-message="Please <a href='#'>upgrade</a>">
<p>This content will show when a premium permit is present, otherwise it shows the message defined in the data-permit-message attribute.</p>
</div>
6. Public API Methods
For the ultimate control on issuing (or revoking) a permit, try the API. You can issue (or revoke) a permit whenever, wherever, and however you want.
|
Method |
Description |
Format |
Example |
|
issuePermit |
Issue a specific permit. The permit parameter must have been specified in the 'permits' setting.
The destination parameter is optional and accepts any relative or absolute url. If the destination parameter is excluded the current page will reload.
|
$.permit.issuePermit( <permit>, <destination> ); |
$.permit.issuePermit('premium', 'thanks-for-upgrading.html'); |
|
revokePermit |
Revoke a specific permit. The permit must have been specified in the 'permits' setting.
The newPermit parameter is optional. Specifying a newPermit will issue that permit to the user as soon as the original is revoked. This might be used in the case of an account downgrade (e.g., from premium to free). If the parameter is excluded, no new permit is issued.
The destination parameter is optional and accepts any relative or absolute url. If the destination parameter is excluded the current page will reload.
|
$.permit.revokePermit( <permit>, <newPermit>, <destination> ); |
$.permit.revokePermit('premium', 'free', 'sorry-to-see-you-go.html'); |
7. Settings & Options
|
Setting/Option |
Description |
Default |
Example |
|
permits |
Object of available states. |
['admin'] |
['free','premium','admin'] |
|
reissueDestination |
Specifies the action to be taken when a new permit is issued using the permits agent. Defaults to a javascript-enabled page reload. Otherwise it redirects to the specified location. |
'reload' |
'dashboard.html' |
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial